Global Comparison - TEQs and PCBs
To understand the degree of contamination by organochlorine
compounds in human breast milk collected from Asian developing
countries, concentrations of these contaminants observed
in this study were compared with those reported from other
countries in 1990s.
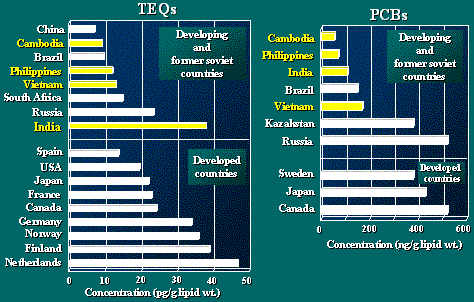
These two figures show international comparison of dioxins
and PCBs concentrations in human breast milk.
Generally speaking, dioxin residue levels were apparently
lower in developing countries than in developed nations.
However, dioxin levels in human breast milk from dumping
site in India were higher than those in
general public from other developing countries, and comparable
to those from developed nations.
So far, it has been believed that the dioxin problem is
a major issue in developed nations. No dioxin contamination
and dioxin problems were known in developing countries other
than some sporadic incidents such as herbicide agent orange
in Vietnam and Yusho disease in Taiwan.
However, as I pointed out here, the dumping sites of municipal
wastes can be a significant emission source of dioxins in
some developing countries like India.
As seen in right figure, PCBs concentrations in human breast
milk from Asian developing countries were lower than those
from developed nations and former social countries.
As a whole picture, except for dumping site in India, contamination
by dioxins and PCBs in human breast milk were higher in
developed nations than in developing countries.
Global comparison of TEQs and
PCBs concentrations
in human breast milk
 |
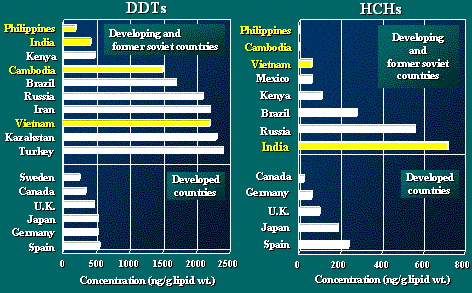
Global Comparison - DDTs and HCHs
These two figures illustrates the comparison of DDTs and
HCHs residue levels in developing and former social countries
with those in developed nations.
As seen here, we can clearly say that contamination by
organochlorine insecticides in human breast milk are much
higher in developing and former social countries than in
developed nations.
Global comparison of DDTs and
HCHs concentrations
in human breast milk
 |
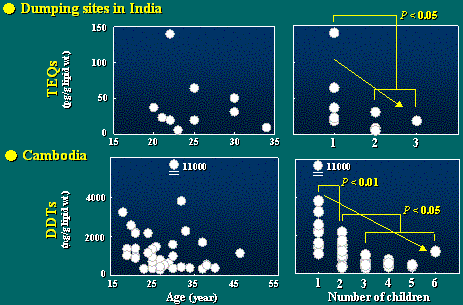
Age and Child - TEQs and DDTs
Earlier studies reported that concentrations of organochlorine
compounds in human breast milk were affected by various
factors, such as woman's age, number of children,
lactational period, ect.
So, we attempted to examine the relationship between concentrations
of organochlorine compounds detected at relatively high
levels in this study and woman's age, and number of
children.
The left two figures show the variation of dioxins and
DDTs concentrations in human breast milk with woman's
age.
As shown here, no significant correlation was observed
with woman's age.
We considered that possible reason for it might be arisen
from various number of children in lactating women.
Hence, the relationship between concentrations of these
contaminants and number of children were examined and given
in the two right figures.
As seen here, dioxins and DDTs concentrations in human
breast milk tended to decrease with increase of number of
children.
This means that organochlorines in mother's body
are significantly excluded by the experience of nursing
lactation and become less.
From this result, we can also guess that the first infants
are exposed to higher levels of organochlorines from breast
milk and might be at relatively higher risk of these contaminants.
This fact was found in developing countries, but it poses
serious problems for humans in developed nations also. Namely,
we can not ignore this fact, since this may be trouble of
some concern.
Relationship between woman's
age, number of children and concentrations of TEQs,
DDTs in human breast milk
 |
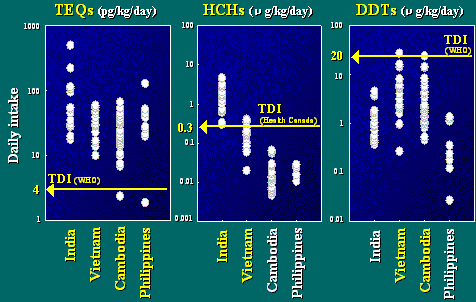
Daily Intake
OK, back to the talk on the pollution in developing countries.
I would like to explain daily intakes of dioxins, HCHs,
and DDTs from human breast milk by infants.
In this figure, the X-axis shows country, and the Y-axis
indicates daily intake.
Daily intakes were calculated, based on the assumption
that an infant ingests 700ml of milk per day and weight
of an infant is 5kg.
The estimated daily intakes of dioxins
by infants in all the four developing countries exceeded
TDI proposed by WHO in 1998.
Furthermore, in Indian infants, the daily
intake of HCHs also exceeded TDI proposed by health Canada
in 1996.
Estimated daily intakes for
infants based on TEQs, HCHs, and DDTs concentrations
in human breast milk
 |
Thyroid Hormone
In order to assess the toxic effects of POPs, we compared
the levels of thyroid hormone and Vitamin A in serum of
blood with dioxin concentrations in breast milk from lactating
woman.
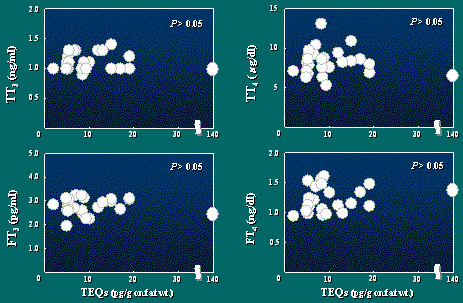
By the result shown in this slide, no significant correlation
could be found for all the thyroid hormones, indicating
less effect of dioxins on thyroid hormones.
Relationship between TEQs concentrations
in human breast milk and thyroid hormone levels in serum
 |
Vitamine A and dioxins in Human
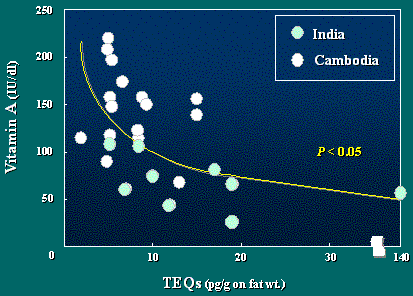
However, as seen here, significant negative correlation
was observed between TEQ concentrations of dioxins
in human breast milk and Vitamin A levels
in serum in the blood from India and Cambodia.
This may suggest an acceleration of vitamin A metabolism
or the inhibition of vitamin A formation by dioxins in human
body.
Relationship between TEQs of
dioxins and related compounds
in human breast milk and vitamin A levels in serum
 |
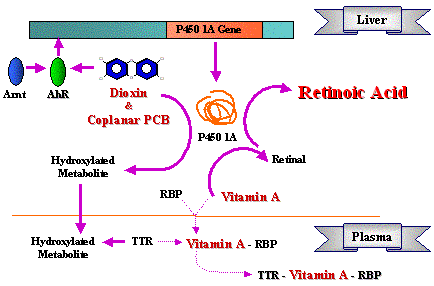
Vitamine A Metabolism
The accelerated metabolism of vitamin A by dioxins forms
active metabolites such as retinoic acid,
and it leads to an imbalance of metabolic contents.
It is well known in the experimental animals that the imbalance
of retinoic acid cause growth retardation,
skin disease and malformation.
Proposed Mechanism of Plasma
Vitamin A Depletion
by Exposure to Dioxins
 |
Deformities (1)
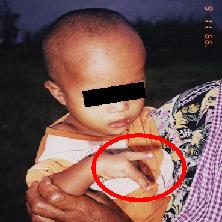 |
In slum near to dumping site, we found
some deformities and diseases, in the people living
there.
This is a case of malformation in fingers.
|
Deformities (2)
This is a case of malformation in legs.
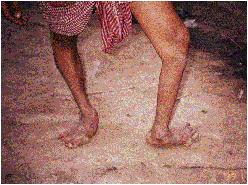
Deformities (3)
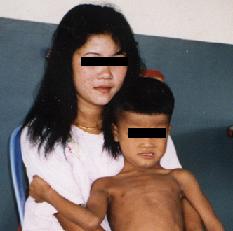 |
We also noticed Intellectual impediment
in some individuals, as in the case of the small boy
you see here. |
Deformities (4)
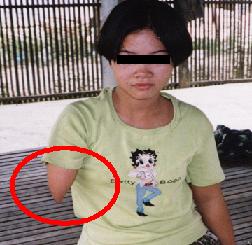 |
This is a case of deficience in leg
and arm.
Of course, we have no clear evidence yet to specify
the cause of these abnormalities, but we should consider
toxic contaminants originating from dumping sites
as one of the possible cause.
The additional epidemiological studies and POPs monitoring
are required in dumping site populations in developing
countries. |
Conclusion - 1
The first, second and third conclusions indicate the widely
contamination by POPs in human breast milk of residents
in Asian developing countries. Particularly, Indian residents
around dumping site were found to highly expose to dioxin
related compounds as well as organochlorine insecticides.
Conclusion - 2
Forth conclusion is that,
The first infant is exposed to higher levels of POPs from
human bresat milk and might be at relatively higher risk
by these contaminants.
Fifth conclusion is that,
The estimated Daily intakes of some POPs by infants in some
developing countries exceeded TDI.
Final conclusion is that,
Significant negative correlation was observed between TEQs
of dioxins in human breast milk and Vitamin A in serum.
It may suggest a part of dioxin effect on the human health
in dumping site.
As I presented on yesterday, very high levels of dioxin
and its related compounds have been found in Malaysian dumping
sites. This result indicates that similar satiation might
be expected in other countries. Thus, further studies are
needed in dumping sites in Asian developing regions, and
emission control for dioxins and PCBs is requested.
Thank you for your attention.
|
