









  |

 |
 |
PCB Symposium 2003 in Malaysia |
|
 |
 |
| China: PCBs
Pollution in China |
 |
|
|
PCBs
Pollution in China
Ms. KeQing Tao
Shanghai Putuo District Environmental Monitoring Central Station
Introduction
PCBs have generally been considered to be one of the
global pollutants.
After the 70's, countries all over the world have
taken steps to halt production and ban or limit the use
of PCBs. The global accumulated amount of PCBs is estimated
to be around 2 million tons. China started the production
of PCBs in 1965 and ceased production at the end of 1974.
Over the years, the accumulated amount has reached 10,000
tons. Of this amount, about 9,050 tons of chlorinated
triphenyls have been used as soakers for transformers
and about 1,000 tons of chlorinated pentaphenyls as additives
in paints. When the PCBs ceased production, the 750,000
transformers containing PCBs were subsequently discarded
as useless in the years 1980 to 1990.
Currently, most of them are being dumped and sealed in
caves or in cellars. However, due to the long term storage,
the rotting process and other damages, PCBs leakages occurred.
The soil surrounding the dumping site has been found to
have a higher content of PCBs.
Report on the areas polluted by the PCBs
A. Test results of the PCBs content in the highly contaminated
areas around the dumping sites of the disused transformers.
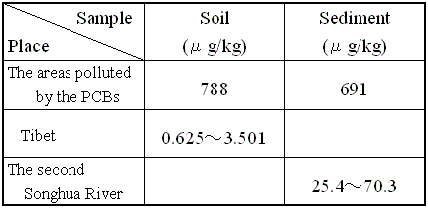
- Soil samples taken around the said areas were found
to contain 788 mg/kg (dry weight) of PCBs. Compared
to the documentary report, the soil in Tibet is not
directly affected by PCBs was found to contain only
0.625 - 3.501 ug/kg (dry wt) of PCBs.
- Samples of the subsoil taken from the rivers around
the contaminated areas were found to contain 691 ug/kg
(dry wt) of PCBs. Compared to the national documentary
report, subsoil picked up from the Songhua River was
found to contain 25.4 - 70.3 ug/kg (dry wt) of
PCBs.
The concentrations of PCBs in soil�and
sediment of various environment
 |
- We collected two samples of the subsoil from the
river, one at the depth of sample A, 0.5 meter and the
other one, sample B at 1 meter.
The PCBs contents of sediment, the depth
of 0.5 and 1 meter from the river
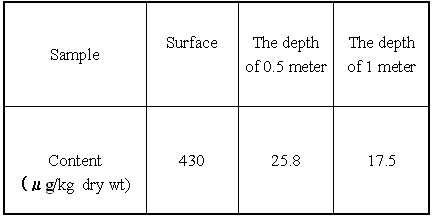 |
Their PCBs content was tested. It was found the sample
A contained 430 ug/kg (dry wt) of PCBs and sample B
contained 17.5 - 25.8 ug/kg (dry wt.).
This shows that as the depth of the subsoil increases,
the PCBs content decreases substantially. The findings
give rise to two other interpretations. Firstly, the
water solubility of PCBs is quite low, and secondly,
the mobility of the PCBs in the subsoil is limited.
- Determination of the PCBs content in the fish muscle
samples collected from different areas.
The concentrations of PCBs in fish tissues
(µg/kg)
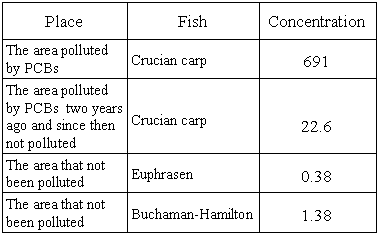 |
Sample 1:
Muscle of carps caught in existing highly contaminated
river: the PCBs content was 691 ug/kg
Sample 2:
Muscle of carps caught in the river which had been
contaminated by PCBs two years ago and since then
unpolluted: the PCBs content was 22.6 ug/kg
Sample 3:
Muscle of Silver Pomfret (Euphrasen) and that of Dragonhead
Fish (Buchaman Hamilton) caught in uncontaminated
waters: their PCBs content was 0.38 ug/kg and 1.38
ug/kg respectively.
It is obvious, therefore, that:
(a) fish caught in the contaminated waters has higher
PCBs content than that in the uncontaminated waters,
and
(b) fish caught in existing contaminated waters had
PCBs content a few hundred or even a thousand times
higher that that in the uncontaminated water.
-
Determination of the total amount of PCBs and other
PCB-related substances in the contaminated water and
that of the fish caught in it.
Percentage composition of PCB congeners
in fish and water
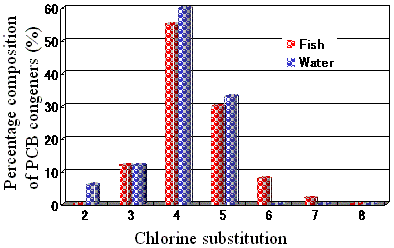 |
Studies showed that the water sample contained PCBs
weighing 2.97 ug/kg. That means the fish muscle sample
is more than 7,000 times higher that that of the water
sample. From the investi8gation done on the distribution
of the other PCB-elated substances, we noticed that
in the water sample, the PCBs content with 2.3 chlorine
substitution was relatively higher, but in the fish
muscle sample, with 6.7 chlorine substitution, the
PCBs content was relatively higher. The reasons are:
(1) PCBs with low chlorine substitution has higher
water solubility, but PCBs with high chlorine substitution
has relatively higher fat solubility; and (2) PCBs
with low chlorine substitution can easily be metabolized
and excreted by aquatic living things but the bioaccumulation
of the PCBs with high chlorine substitution in the
bodies of the aquatic living things is more stable.
From the analysis of the fish muscle samples, we discovered
five types of PCB-related substances with higher toxic
level but in the water sample, there was only ONE. The
PCB content in the fish muscle sample was 2.31 ug/kg
but that in the water sample was 0.06 ug/kg. Hence,
we can infer that aquatic living things have a high
rate of bioaccumulation in their bodies not only for
PCBs but also for highly toxic PCB-related substances.
- Determination of PCB content in the muscle, liver,
bile and egg of the female carp caught in the contaminated
river.
Concentration of PCBs in various fish
organs
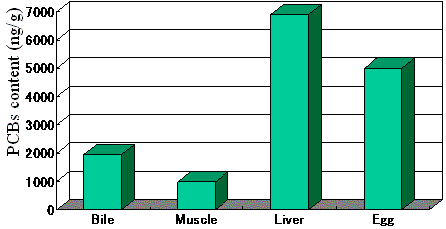 |
(A) The results indicated that the PCB content in the
fish body followed a distribution trend of liver >
egg > bile > muscle. The PCB content of the fish's
liver was 8 times that of the muscle.
(B) Results of the second investigation into the PCB
content conducted in the Songhua River.
Preliminary investigation into the drainage system along
the river revealed no direct source of PCB pollution.
Concentration of PCBs in water, sediments
and fish of second Songhua River with no direct source
of PCB pollution
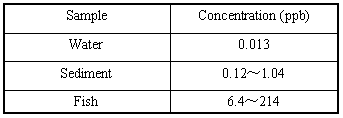 |
Investigation Results:
- Rate of PCBs contamination of the river water was
31.5% and the average concentration rate was 0.013 ppb.
- Rate of PCBs contamination of the subsoil was 100%
and the concentration rate was 0.12-1.04 ppb, the average
value being 0.62 ppb.
- Rate of PCB contamination of the fish body was 100%,
the concentration rate was 6.4-214 ppb.
This showed that the concentration rate in the river
water was not high but that in the fish body was much
higher, the bioaccumulation rate was more than 10,000
times.
- Investigations done on the different body parts of
the fish revealed that the PCB content in the liver,
brain and other high-fat organs was significantly higher.
(C) The condition of pollution in the well-preserved
primitive environment of Tibet's South Kabawa hilly
regions.
The concentrations of PCBs in Tibet's
South Kabawa hilly regions (ppb)
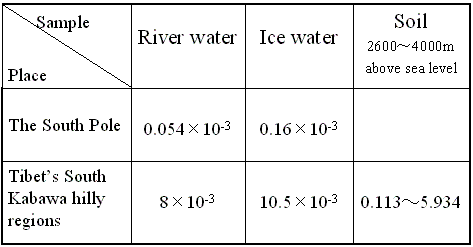 |
Investigations showed little PCB content in the river
water and ice water. The PCB content in the ice water
was 0.0105 ppb and that of the river water was 0.008 ppb,
meaning ice water PCB content was slightly higher than
that of the river water. The date, when compared to that
of the documentary report on the South Pole's ice
water, lake water and sea water, showed higher level of
PCB contamination.
The different types of soil of the grassy marshland,
from 2,600 meters to 4,000 meters above sea level were
found to have different degrees of PCB pollution, their
PCB content ranging from 0.113-5.934 ppb.
The above information clearly indicates that PCB pollution
has extensively affected our environment and it is time
for all of us to take this matter seriously.
Lately, our government has taken further steps to solve
the problems of PCBs pollution. They are:
- To include PCBs in the list of "National Hazardous
Substances" and to introduce new regulations for
their control.
| a. |
All PCBs-related wastes are subjected to special
treatment. |
| b. |
Factories have to apply to the relevant authorities
for approval for the use of PCBs. |
| c. |
To ban the transit of PCBs wastes through Chinese
territory. |
- To set permitted value for PCBs content in waste materials
at 50mg/kg.
- To dispose of waste materials with PCBs content of
50-500mg/kg at designated dump sites or landfills. Those
with PCBs content above 500mg/kg must be disposed of
by using high temperature combustion technology. PCBs
wastes that are not suitably treated must be collectively
and safely stored or sealed at designated sites according
to the instructions of the relevant authorities.
- To formulate regulations to control the import of
used products containing PCBs. Those with PCBs content
higher than the permitted value will not be allowed
entry into country.
We believe from now on, more and more laws and regulation
will be enacted and stricter enforcement measures will
be taken to curb the menace of PCBs pollution in China.
|
|
|
