









 |

 |
 |
PCB Symposium 2002 in Japan |
|
 |
 |
| Country report
from Japan |
 |
|
|
Page 1 2 3
4
 |
Country report from Japan
I talk about situation of PCBs in Japan |
The Use of PCBs
PCBs were used in insulating oils of transformers, condensers
and capacitors, lubricating oil, plasticizer, carbonless
duplicating papers, and paints.
Uses
|
Examples of
products, and the places they are used |
| Insulating
oil |
For transformers |
Transformers for buildings,
hospitals, railroad vehicles, vessels, etc. |
| For capacitors |
Capacitor for fluorescent
lights and mercury lamps. Household electrical
appliances, such as air-conditioners, washing
machines, monochrome television sets, and microwave
ovens.
Fixed paper capacitors for motors, capacitors
for direct currents, capacitors for accumulation
of electricity . |
| Heat medium (heating
and cooling) |
Heating and cooling agent
in various chemical, food, synthetic resin industry.
Preheating agent of the fuel oil of vessels, central
heating systems, and panel heaters. |
| Lubricating oil |
Lubricating oil for high temperature,
fluid for oil-hydraulic circuits, vacuum pump
oil, etc. |
| Plasticizer |
For insulation |
Covering and insulating tape
of an electric wire. |
For resistances to
flame
|
Mixed to polyester resin,
polyethylene resin, rubber, etc. |
| Others |
Mixed to adhesives, varnish,
wax, and asphalt. |
| Dot impact printer |
Non carbonic papers (solvents),
electronic type copying papers |
| Paints and printer
inks |
Paints for fire-resistance,
corrosion-resistance, chemical-resistance, and
waterproof. Printer inks. |
| Others |
Coating of papers, sealants
of cars, coloring of china glassware, color television
parts, the effect extension agents of agricultural
chemicals, oil additive agents. |
|
Ministry of Environment (2001); "For proper processing
of polychloro biphenyl (PCB) waste."
Pamphlet.
These pictures (transformer, condenser, and capacitor)
are typical equipments that uses PCBs. I talk about how
much these equipments exist in Japan, next slide

Transformer |

Condenser |

Capacitor |
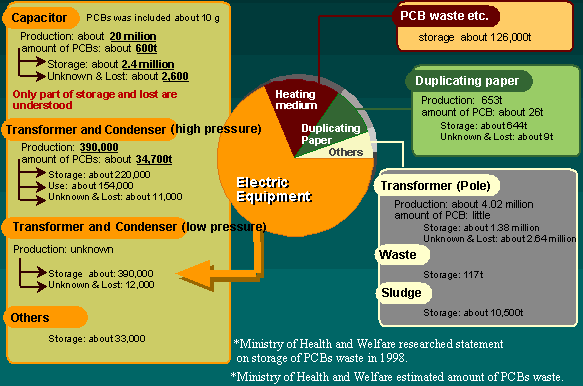
The amount of PCBs used and stored
This figure shows the amount of PCBs used and stored. I
got this information from the Ministry of Health and Welfare's
report of 1998. Since this report is imcomplete, there may
be other PCBs which is not on this data. However, for now
I use these data. Further research is necessary.
The amount of PCBs produced in Japan is 58,787 tons, 54,001
tons of them are reported to be in use or used inside the
country. PCBs are mainly used in electric equipment, It
is about 70%.
Among electric equipments in high pressure transformer and
condenser, large amount of PCBs are used, it is about 34,700
tons. High pressure transformer and condenser was produced
about 390,000, of which, 11,000 are unknown or lost. This
is a big problem.
The production of low pressure transformer and condenser
are unknown.
The amount of PCBs in fluorescent right capacitors are 600
tons, it is small than transformers and capacitors. But
the amount of production are 20 millions, the amount lost
was much bigger than capacitor. Although capacitor contains
small amount of PCBs content, the amount of production and
lost are large. Therefore, capacitor a source of PCBs contamination
too.
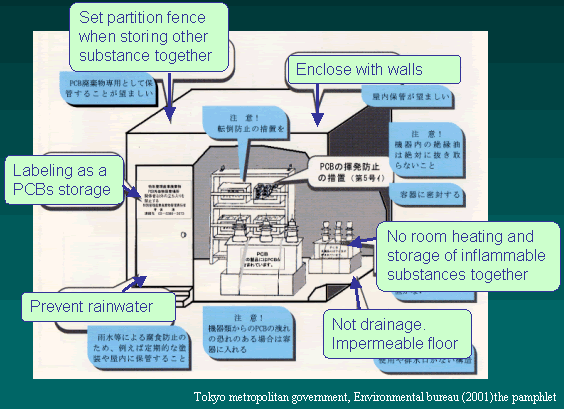
The methods of PCBs storage
Since PCBs detoxification treatments are not being conducted
in Japan, all PCBs equipments that passed their expiry dates
must be stored. According to the Waste Management Law, the
storage of PCBs should be registered and the storage area
should be arranged in the following ways;
- Enclose with walls
- Labeling on an easily recognized place
- Example: <labelling on equipments> This equipment
contains PCBs
- Example: <labelling on storage facility> PCBs
waste storage area
- Not drainage and system impermeable floor
- Set partition fences when storing other substances together
- No room heating and storage of inflammable substances
together
- Prevent rainwater
Not only to avoid the loss of equipments during storage,
detoxification treatment of PCBs must be conducted as soon
as possible since the risk of PCBs leakage during the storage
is estimated to be larger than the risk of leakage in the
process of treatment.
The treatment of PCBs wastes
In Japan, the impact of the Kanemi Usho Case kept residents
away from the approval of the construction of PCBs disposition
facilities. However the government had set a goal last year
(2001) to complete PCBs disposition in 15 years.
PCBs detoxification treatments conducted in Japan are only
two cases. The first one is a high temperature decomposition
conducted during 1987 to 1989 by Kaneka Industries, a corporation
which had been producing PCBs in the past. 5500 tons of
PCBs which had been used as heat exchange media were incinerated
at a temperature above 1100 . .
The second case was a disposition of carbonless duplicating
paper. 1778 tons were incinerated on ships in Tokyo Bay.
However no further disposition has been conducted because
of the opposition from the residents.
Many people do not support PCBs disposition by incineration,
maybe because incineration facilities emit dioxins. The
government allowed the application of chemical treatment
method.
This year, Kita-Kyushu City expressed the acceptance of
the construction of a PCBs disposition facility. It has
not been decided which method of disposition will be adopted
in this facility; a discussion is going to be held among
people including specialists and residents.
The law about PCBs
I introduce the law about PCBs.
In Japan, PCBs began to be produced in 1954. The Kanemi
Yusho Case occurred in 1968. In 1974, production, import,
and new use of PCBs were banned substantially and the storage
of old PCBs equipments that passed their lifetime period
became obligation.
However as I told before it was difficult to build facility
for treatment. So the amount of PCBs waste are increasing,
partly lost.
The movement of elimination POPs (Persistent organochlorine
Pollutants) such as PCBs is developing in worldwide, POPs
treaty adopted in 2001. The countries which ratified POPs
treaty must eliminate by 2028.
This worldwide current movement prompted, Japanese government
to work earnestly on PCBs disposition. The Law Regarding
Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCBs Wastes was enacted
in June 2001. By this law, the registration of the use and
the storage of PCBs became mandatory to prevent the loss
of PCBs equipments and to promote detoxification treatment.
The law about PCBs
 |
 |
| 1929
|
Swan Company, which
merges with Monsanto Company afterwards,
begins the production of PCBs in the United States
|
| 1954
|
The production of PCBs starts
in Japan.
(Kaneka Industries starts the production this
year.
Then in 1969, Mitsubishi Monsanto Company.) |
| 1968
|
The Kanemi Usho Case occurs
in Japan.
The poisonous characteristics of PCBs become a
serious social issue |
| 1972
|
The Japanese Ministry of International
Trade and Industry
prescribes the industries to stop the production
of PCBs and to collect PCBs. |
| 1974
|
The Law Regarding Safety
Assessment and
Production of Chemicals enacted in Japan.
(It forbids production, import, and the new use
of PCBs.) |
| 1976
|
Incineration at high
temperature is suggested as one of the disposition
methods
in Waste Management Law in Japan |
| 1987-89
|
Incineration of 5500
tons of liquid PCBs
were done by Kaneka Industries at Kousa Plant
|
1992
|
PCBs were specified as Industrial
Wastes Subject to Special Control in Japan |
| 1998
|
1998 Chemical treatment was
added as a disposition method
in Waste Management Law in Japan |
| 2000
|
New chemical decomposition
treatment was added to the disposition methods
in Waste Management Law. Millennium Project starts
in Japan
December - POPs treaty agreed in Johannesburg
|
| 2001
|
May - POPs Treaty adopted
in Stockholm
June - The Law Regarding Promotion of
Proper Treatment of PCBs Wastes enacted in Japan
October - amend the law electric business |
 |
 |
|
Start to report on PCBs storage
The owner of the equipment containing
PCBs have to register the amount of stored PCBs waste and
stored situation.
The government made pamphlet, and appealed to owners of
PCBs for registration. These are the pamphlets made by the
ministry of the environment, Tokyo and Tochigi.
The mandatory registration has just started recently. Most
owners don't know about the registration. The government
is puzzled how to tell owners. It is a big challenge for
the government to let all owners know about the registration
in order to get a clear picture of how much PCBs is stored.
 |
 |
 |
Ministry of the environment
|
Tokyo
|
Tochigi |
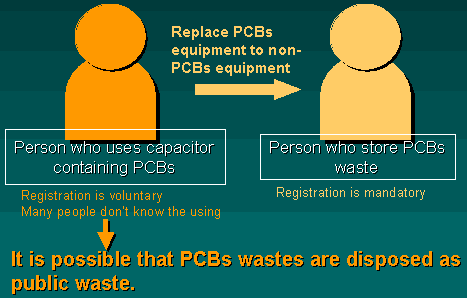
Issues concerning the laws/ regulations
'The current law regarding promotion of proper treatment
of PCBs wastes' is effective for stored PCBs waste. But
it is not effective for capacitors.
If people who uses PCB equipment changed with a new one
without PCB, he has to store the old PCBs equipment, thus
owners of PCBs have to register the amount of stored PCBs.
But the person who use PCBs equipment don't need to register.
Therefore the person may even don't know they are PCBs owners.
Their equipments may be disposed as a municipal waste. Then,
PCBs contaminate the environment.
Current issues in Japan
I summarize current issues in Japan.
The amount of PCBs equipment is unknown. The amount of
PCBs is also unknown.
The detoxification treatment of PCBs has been proceed.
There are few regions that accept planning of PCBs treatment
facilities.
The public don't understand the issue of PCBs.
PCBs pollution is under way, now
I talk about the action by Japan Offspring Fund to next
slide.
|
Page 1 2 3
4
|
|
