









 |
 |
| Pollution of
human beings is on going |
 |
|
|
As a matter in fact, we humans are taking in
PCBs everyday. The main route is via foods. Foods become contaminated
with PCBs because there are a lot of PCBs in the environment.
PCBs have, and are at this moment, leaching out of products
in our daily lives, such as the capacitors in fluorescent lights
and transformers. And those PCBs that are emitted come back
into our daily lives in a form of foods.
After we consume PCB-contaminated foods, they are absorbed into
our bodies via our gastrointestinal tract and they accumulate
in fatty tissues. They are then passed on from mothers to babies
during pregnancy and breast-feeding. Breast-feeding plays an
essential role in nurturing babies and in the transmission of
immunities from mothers to their children. For this reason,
mothers should try as much as possible not to consume PCBs during
pregnancy and lactation periods.
To stop further contamination of foods, we must cut off the
sources of PCB pollution and conduct collection and treatment
of PCB wastes.
Average daily intake of PCB (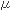 g/person)
in various countries. g/person)
in various countries.
 |
 |
 |
Country
|
Year |
Intake |
 |
 |
 |
Gujarat, India
|
1980s
|
ND |
Punjab, India
(vegetalian)
|
1980-1981
|
ND |
Punjab, India
(non vegetalian)
|
1980-1981
|
ND |
Uttar Pradesh, India
|
1981-1983
|
ND |
India
|
1989
|
0.86 |
Gujarat, India
|
1990s
|
ND |
Thailand
|
1980
|
ND |
Thailand
|
1989
|
1.5 |
Vietnam
|
1990
|
3.7 |
Japan
|
1977
|
3.3 |
Japan
|
1985
|
4.3 |
Japan
|
1992-1993
|
ND |
China
|
1973
|
ND |
China
|
1990
|
ND |
Hong Kong
|
1985
|
ND |
New Zealand
|
1982
|
54 |
Australia
|
1980
|
ND |
Australia
|
1990-1992
|
6.9 |
USA
|
1980
|
0.45 |
USA
|
1987
|
1.6 |
USA
|
1990
|
ND |
Canada
|
1985
|
0.09 |
Sweden
|
1975
|
9.2 |
Sweden
|
1990
|
6.8 |
Finland
|
1983
|
14 |
West Germany
|
1987
|
4.1 |
Italy
|
1971-1972
|
ND |
Italy
|
1978-1984
|
ND |
UK
|
1980
|
ND |
UK
|
1985
|
ND |
| UK |
1990s
|
0.53 |
Spain
|
1979-1980
|
ND |
Spain
|
1980-1981
|
ND |
The Netherlands
|
1976-1978
|
ND |
Switzerland
|
1981-1983
|
ND |
 |
 |
 |
|
K. Kannan et al., (1997) Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol
152, 1-55
Concentrations of PCBs in butter samples
 |
 |
Country
|
Mean(pg/g
lipid) |
 |
 |
Austria
|
6,810 |
Austria
|
740 |
Brazil
|
1,060 |
Canada
|
1,680 |
Brazil
|
1,790 |
Czeck Republic
|
14,090 |
Denmark
|
3,050 |
Germany
|
8,740 |
India
|
4,510 |
Israel
|
3,570 |
Italy
|
7,660 |
Japan
|
600 |
Mexico
|
1,180 |
Philippines
|
520 |
S. Africa
|
4,160 |
Spain
|
5,470 |
Sweden
|
3,610 |
Thailand
|
1,210 |
Netherland
|
5,620 |
New Zealand
|
230 |
Tunisia
|
11,810 |
U.K.
|
3,370 |
U.S.A
|
2,250 |
 |
 |
|
O. I. Kalantzi et al., (2001) Environ. Sci. Technol, 35,
1013-1018
|
Concentration of PCBs in foodstuffs
(ng/g wet wt.)
 |
 |
 |
Food
|
Countris
|
Conc. |
 |
 |
 |
Animal fat
|
Vietnam |
61 |
Beef liver
|
South Korea |
5.4 |
Beef muscle
 |
South Korea |
3.7 |
Beverages
 |
Australia |
2.3 |
Butter
|
Vietnam |
17 |
Carp
|
South Korea |
5.6 |
Carp fish
|
Indonesia |
NA |
Caviar
|
Vietnam |
51 |
Cereals
|
Australia |
0.62 |
Cheese
|
Papua New Guinea |
4.4 |
Chicken
|
Solomon Islands |
5.2 |
|
Papua New Guinea |
124 |
Chicken muscle
|
Indonesia |
4.5 |
|
Indonesia |
NA |
Croaker
|
South Korea |
60 |
Dairy products
|
Australia |
4.1 |
Egg
|
Indonesia |
NA |
Fish
 |
Australia |
55 |
|
Indonesia |
3.8 |
|
Solomon Islands |
3.6 |
|
Vietnam |
10 |
Fish and shellfish
 |
Papua New Guinea |
7.5 |
Fruits
 |
Australia |
0.28 |
Meat
 |
Vietnam |
18 |
Meat and fat
|
Australia |
11 |
Oil
|
Vietnam |
21 |
|
Australia |
6.5 |
Pork
 |
South Korea |
2.2 |
Pork fat
|
Indonesia |
2.9 |
|
Papua New Guinea |
45 |
|
Solomon Islands |
17 |
Pulses
 |
Australia |
1.4 |
|
Vietnam |
4 |
Rice
 |
Indonesia |
0.34 |
|
Vietnam |
2.5 |
Shellfish
|
Vietnam |
27 |
Squid
 |
Indonesia |
2 |
Vegetable
 |
Australia |
0.4 |
|
Indonesia |
NA |
 |
 |
 |
|
K. Kannan et al., (1997) Rev. Environ. Contam. Toxicol
152, 1-55 |
|
|
|
