 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
| |
 |
|
Japan
|
Malaysia |
Hong
Kong |
Taiwan |
korea |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
|
 |
When
was the production of PCBs banned?
|
1972 |
PCBs
are not manufactured in Malaysia
|
According
to the information from the Environmental Protection Department(EPD)
of the HKSAR, no existing environmental legislation currently
bans the production of Polychlorinated Biphenyls (PCBs)
in Hong Kong. EPD is also not aware of any existing factory
producing PCBs here. In Hong Kong, PCBs are mainly used
in transformers and capacitors installed many years ago
but they are being phased out voluntarily by owners.
|
1980 |
1996
(Toxic Chemicals Control Law) |
Total
PCBs produced?
|
58,787ton |
- |
No information
available.
|
Unknowing |
never
manufactured in Korea |
When
was the import and export of PCBs banned?
|
1974 |
1998 |
Under
the Waste Disposal Ordinance (WDO), Cap.354, Law of Hong
Kong, import or export of PCBs waste requires a permit
from EPD. To tie in with the requirements of the Basel
Convention, import of PCBs waste from developed countries
into HK has been banned since 28 Dec 1998. It should be
noted that the WDO does not control import and export
of PCBs goods and products.
|
1982 |
1996
(Toxic Chemicals Control Law) |
How much
PCBs were imported/
exported?
|
1,048ton/5,318ton |
No data
|
There
is no information about the import/export of PCBs goods
and products. However, EPD has not received any permit
applications for import and export of PCBs waste since
the implementation of the WDO control on 1.9.1996. Under
Basel Convention, EPD has issued 4 transit consents on
the transshipments of "Waste containing PCB"
from Korea to Netherlands for recycling. So far, about
260 tonnes of PCB wastes has been passed through Hong
Kong under these 4 consents.
|
Import:
unknowing / Export: 0
|
- |
Is the
use of products containing PCBs banned?
|
NO
The products made before 1974 are allowed to use.
|
i) NO
ii)The products made before 1998 are allowed to use PCB |
NO
|
NO
The capacitors produced before 1982 are allowed to use. |
YES
The production, the import, the use of the products containing
PCBs over 0.005% is banned |
What
laws/regulations are there for the management of PCBs
?
|
YES.
*The law Regarding Safety Assessment and Production of
Chemicals (1974).
*The Law Regarding Promotion of Proper Treatment of PCB
Wastes(2001).
*Waste Management Law (1976)
|
YES
*The Environmental Quality (Scheduled Waste) Regulation
1989.
*The Environmental Quality (Prescribed Premises) (Scheduled
Waste Treatment and Disposal Facilities) Regulation 1989.
*The Environmental Quality (Prescribed Premises) (Scheduled
Waste Treatment and Disposal Facilities ) Order 1989.
|
*CAP
354 The Waste Disposal Ordinance (WDO), Law of Hong Kong
enacted in 1980.
|
"YES
*Toxic Chemical Substances Control Act
*Waste Disposal Act
* The identification criteria for hazardous industrial
wastes
* The Criteria of Governing Methods of and Facilities
for Storage, Clearance and Treatment of Industrial Wastes
* The Hazardous Industrial Waste Import, Export, Transit
and Transshipment Management Measures"
|
YES
*Toxic Chemicals Control Law
*Waste Management Law
*Electronic Business Act
--allowed transformers which installed before '79.8.30 |
Are the
current laws/regulations sufficient? What should be improved?
What kinds of loopholes exist?
|
No,it
is not sufficient. The current law can not prevent the
loss of capacitors of fluorescent lights which are still
in use.
|
The laws
are only for PCBs generated industrially
|
There
should be more consumer education on how to identify equipments
or flourescent lightings that contain PCBs and how these
products should be disposed in due course.
|
No,it
is not sufficient. The current law can not dispose and
prevent the loss of PCB from wasst equipments containing
PCB below 50 ppm. Because the waste containing PCB below
50 ppm is discarded as municipal waste. |
- |
Has your
country signed/ ratified POPs Convention?
|
NO/NO |
NO |
The Stockholm
Convention has not come into effect yet. HKSAR has not
signed/ratified this convention.
|
NO/NO |
YES/NO |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Are there
any data on the amount and location of PCB equipment currently
in use ?
|
YES/NO.
Some Researches have done. But not enough.
|
NO |
EPD is
currently conducting a survey of PCB equipment currently
in use in Hong Kong and hopes that the results will be
available by late 2002.
|
NO/NO |
Formally,
there are no PCB equipments in use |
Are there
any data on the amount of PCB wastes?
|
YES/NO.
Researches have been done, but not enough. Transformers
and capacitors (37,156 tons).Carbonless duplicating papers
(8,260 tons)
|
NO |
No information
available.
|
NO/NO |
YES/NO
the amount of PCB waste is confirmed 29ton(supposed to
be exported to Netherland)
But, it is possible that more PCB waste exists.
|
Have
capacitors of fluorescent lights containing PCBs been
replaced with non-PCB capacitors?
|
NO.(PCB
capacitors in public facilities will be changed with non-PCB
capacitors by March 2002.)
|
NO |
According
to the EPD, PCB capacitors and transformers are being
gradually phased out and replaced by non-PCB ones.
|
YES |
Formally,
PCB capacitors in public facilities were changed with
non-PCB capacitors |
Are there
any possibilities that PCB wastes are discarded as non-toxic
municipal wastes?
|
YES |
YES |
Yes,
if the owner is unaware of whether the waste contains
PCBs.
|
YES |
YES |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
Are there
any PCB detoxification treatment facilities?
|
NO(In
2004, a facility will be built.) |
YES |
Yes,
the Chemical Waste Treatment Centre.
|
NO
|
YES |
How many
PCB treatment facilities exist?
|
There
is a PCB treatment trial facility.
|
Only
1
|
At present,
the Chemical Waste Treatment Centre is the only facility
treating PCB waste.
|
Four
|
two facilities
in Ulsan and Kunsan
|
What
kind of detoxification method is used ? High temperature
decomposition (incineration) or chemical treatment?
|
Chemical
treatment is promoted.
|
High
temperature decomposition
|
The recommended
method of safe disposal of PCBs is by incineration at
temperature above 1,100 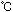 with a mean residence time of 2 seconds and a minimum
excess oxygen content of 3%.
with a mean residence time of 2 seconds and a minimum
excess oxygen content of 3%.
|
Incineration
|
high
temperature decomposition
|
How much
PCBs have been treated so far?
|
about
5,500tons of liquid PCBs , about 1,778 tons of carbonless
duplicating papers (incineration)
|
Since
1998 about 5.28 tons of PCBs are disposed of at this facility.
|
About
40 tonnes of PCB wastes have been treated since 1993.
In the last 3 years (1999 to 2001) about 500 kg have been
treated.
|
Unknown
|
187tons
(18tons were incinerated and the rest were exported) |
How much
PCBs can be treated annually at facilities?
|
-
|
No information
|
The PCB
waste in Hong Kong is often found as insulating oil in
electrical capacitors. The dismantling, shredding and
handling of the waste limits the treatment to no more
than a few tonnes per month. If the PCB oil is removed
from the equipment and packaged in drums, the destruction
rate can be much higher. |
Unknown
|
- |
Has the
government set a goal year for the completion of PCB treatments?
|
2016 |
Not yet
|
The disposal
of PCB equipment is subject to the control of the WDO
as PCB waste is produced. However, the Ordinance does
not stipulate a deadline for disposing of PCB equipment
as long as the waste will be properly treated in accordance
with the chemical waste control requirements. Many local
PCB equipment owners such as power companies have already
phased out such equipment voluntarily and the remaining
number of such equipment in Hong Kong is small.
|
NO |
- |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
To what
extent, are public interested in the issue of PCBs?
|
Only
a part of public knows about the issue. It is important
to raise public awareness.
|
The public
are unaware of what PCBs are and where they are found.
|
Public
are more aware about the hazardous of PCBs in food than
the importance of properly disposing PCBs containing equipment.
It is important to raise public awareness on this issue.
|
Only
a part of public knows about the issue. It is important
to raise public awareness. |
Only
a part of public knows about the issue. |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
 |
