









  |

 |
 |
PCB Symposium 2003 in Malaysia |
|
 |
 |
| Project : Contamination
of dumping site in Malaysia |
 |
|
|
Page 1 2 3
Contamination by polychlorinated biphenyls
(PCBs), dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and dibenzofurans (PCDFs) in soils
from dumping sites of municipal wastes in Malaysia
Mafumi Watanabe1, Mami Niida2, Hatijah Hashim3,
Shinsuke Tanabe1
- Center for Marine Environmental Studies,
Ehime University, Japan,
- Japan Offspring Fund, Japan,
- Consumers Assosiation of Penang (CAP),
Malaysia
|
|
Backgrounds
Thank you Mr. Chairman for introducing me. Good morning
everyone.
First, I acknowledge to Japan fund global environment,
Japan Offspring Fund and Consumers Association of Penang
for inviting me in this symposium.
Today, first of all, I would like to touch on some basic
information of PCBs and its related compounds, polychlorinated
dibenzo-p-dioxins (PCDDs) and dibenzofurans (PCDFs).
And then, I would like to talk about our resent study,
regarding on Contamination by PCBs, PCDDs and PCDFs in soils
from dumping sites of municipal and industrial waste in
Malaysia.
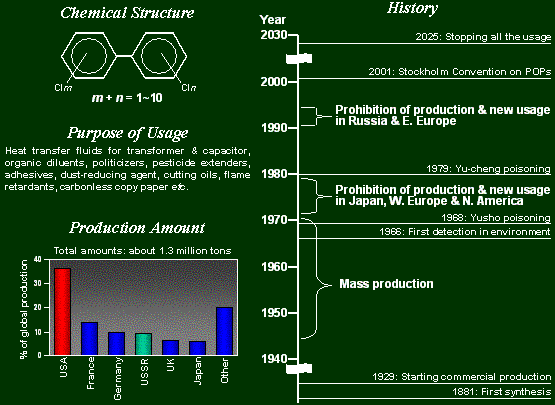
Basic information of PCBs
Here I show the basic information of PCBs. PCBs consist of 209 congeners with different numbers and
positions of chlorine atoms on the biphenyl ring as shown
here.
This chemical was firstly synthezed in 1881, and commercial
production was started in 1929 in USA. Then after, Mass
production was started in late 1940s for industrial proposes,
such as heat transformer oils for transformers and capacitors,
organic diluents, pesticide extenders, dust-reducing agent,
cutting oils, flame retardants, carbonless copy paper and
other.
PCBs have been detected from wild animals since 1966, and
2 case of mass poisoning caused by feeding rice oil contaminated
with PCBs were occurred on 1968 and 1979. Because of these,
Production and new usage was banned in Japan, western Europe
and North America in 1970s, and in Russia and eastern Europe
in early 1990s.
Recently, PCBs were classed into POPs (persistent organic
pollutants), and UNEP request All the PCB usage should be
stopped until 2025.
Until prohibition, PCBs were produced about 1.3 million
tons in the world. As shown here, more than 30% of total
production was in USA, followed by France, Germany, former
Soviet Union, UK, and Japan. Production in other countries,
such as Southeast Asia, Africa and south America, is less
information.
Although most of production and new usage was terminated
30 years ago, why PCBs have been of a great concern as environmental
contaminants, now?
What's problem of PCB contamination?
This is answer.
PCBs have persistent nature in the environment, bioaccumulated
in humans and wildlife, and transported on worldwide by
air and water.
In addition, PCBs have been leakage from transformers and
capacitors, which have been still used or stored.
As these results, PCBs have been detected in all the environmental
media and biota at the highest level among POPs.
Furthermore, PCBs elicits various toxicities, such as body
weight loss, dermal lesions, hepatotoxicity, suppression
on immune system, endocrine disruption, reproductive and
development toxicities, neurotoxicity and carcinogenicity.
These lead that PCBs have been of a great concern as environmental
contaminants.
By the way, most of PCB toxicities are considered to be
caused by coplanar PCBs and polychlorinated dibenzofurans
(PCDFs), which are contained as impurities in commercial
PCBs.
Dioxin-related compounds (DXNs)
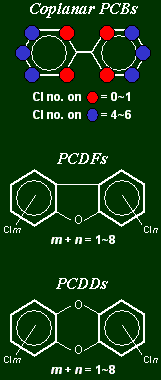 Coplanar
PCBs, PCDFs and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (PCDDs)
are called dioxin-related compounds. Coplanar
PCBs, PCDFs and polychlorinated dibenzo-p-dioxin (PCDDs)
are called dioxin-related compounds.
These compounds are formed as unwanted byproducts
during synthesis of a wide array of commercial chemical
products, such as PCBs and organochlorine pesticides.
In addition, a variety of combustion processes, for
example burning of municipal waste, lead to continuous
formation of dioxin-related compounds, especially
PCDDs and PCDFs.
Due to their persistent nature in the environment,
bioaccumulation in high trophic animals, long-range
transport on global scale by air and water, and highly
toxic effects to human and wildlife, many developed
nations have conducted comprehensive investigations,
controlled emission sources, and applied the environmental
standards for dioxin-related compounds.
As these results, It made clear that environmental
residue levels have been decreasing in recent past
decades.
However, in developing countries, fewer information
are available on the pollution of these contaminants.
|
This is a view of the dumping site of municipal wastes
in Phnom Penh, Cambodia.

This is a same view in India.
Large scale dumping of municipal wastes is common in the
urban regions of many developing countries.
Variety of wastes including plastics, metals, papers, woods
and raw materials are dumped in large open land areas.

The major problem here is burning of wastes at low temperatures
due to the generation of methane gas.
As you guess now, the burning of wastes forms dioxin-related
compounds.

Slum
Other problem in such dumping site is presence of slum.
Poor peoples form a slum near to the dumping site, collect
the recyclable and usable items in this area, and keep them
near their houses, as you can see here.

Waste Picker
They are exposed to dioxin-related compounds here, because
they spend most of their time here, and thus seem to be
at risk of many toxic chemicals.

In addition, As you see here, some domestic animals, such
as cows, feed in dumping site.
It can be expected that they are also exposed to dioxin-related
compounds.
Consequently, People, who eat and drink food from these
animals, is exposed to dioxin-related compounds.

Dioxin-related compounds
 |
From the slides I showed now, dumping sites of
municipal wastes in Asian developing countries may
be expected as the sites of secondary formation of
dioxin-related compounds, because huge amounts of
various wastes have been dumped daily and continuously
burned under low temperature by spontaneous combustion
or intentional incineration.
Therefore, it is suspected that pollution sources
are present in dumping sites. As results, DXNs from
here will be contaminated surrounding fields, and
many residents and wildlife around there might be
exposed to these contaminants. |
Malaysian picture
We have also found similar dumping site of municipal and
Industrial wastes in Malaysia on last Survay.
This shows the combustion of solid waste in dumping site
in Malaysia.
However, to our knowledge, there is no information on contamination
by dioxin-related compounds in such field in Malaysia.

|
Page 1 2 3
|
|
